The Synergy between Industrial Air Compressors and Geogrid Types
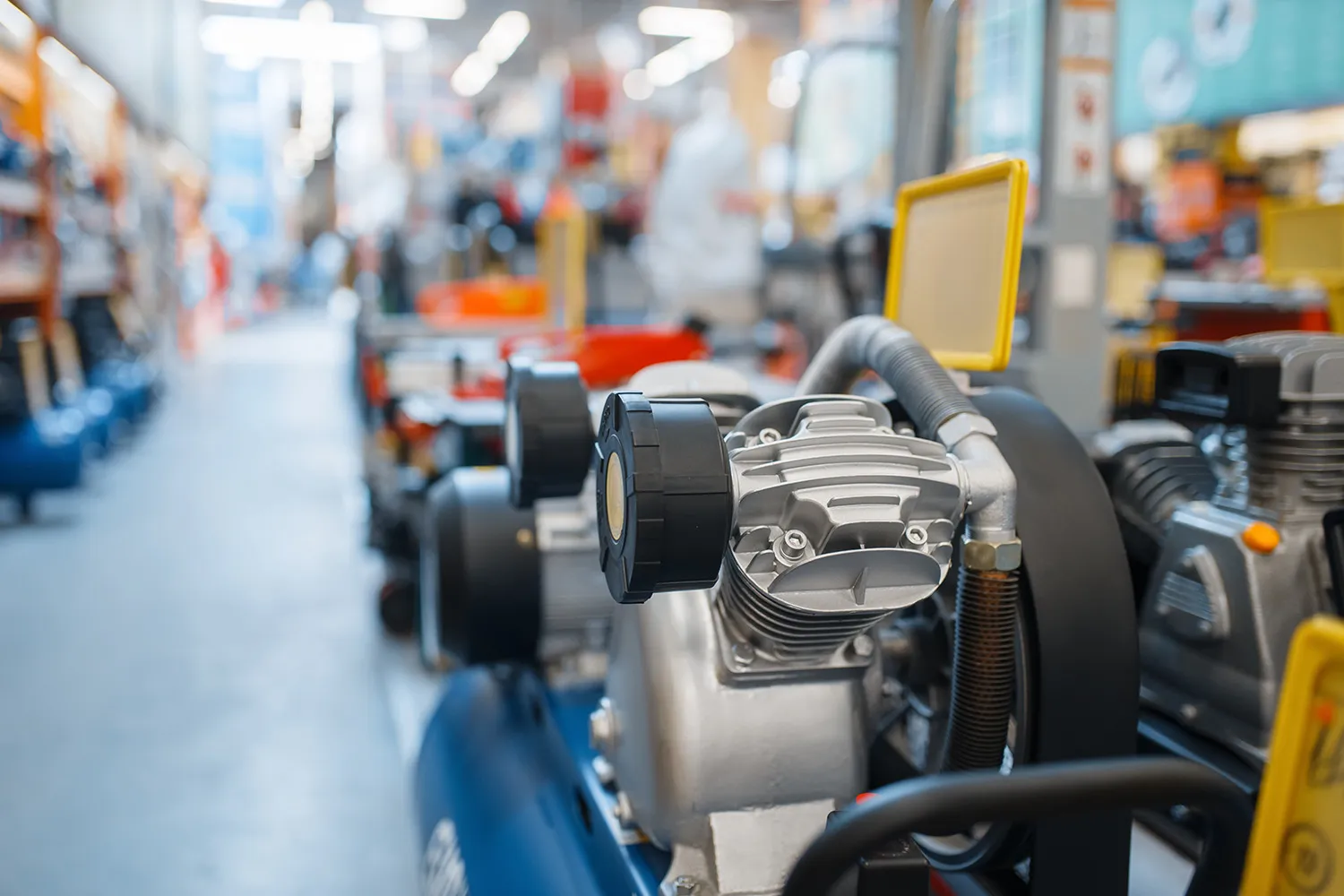
An industrial air compressor, a cornerstone of mechanical engineering, functions as a vital tool to generate pressure within compressible fluids or gases, with air being the most prevalent medium. Across industries, these compressors serve multifaceted purposes:
- Supplying instruments or shop air
- Empowering a spectrum of air tools, abrasive blast equipment, and paint sprayers
- Facilitating refrigeration and air conditioning transitions
- Propelling gases through complex pipelines
Comparable to pumps, compressors are categorized into positive-displacement or centrifugal mechanisms. Unlike pumps, which tend to be predominantly centrifugal, compressors primarily operate within the positive displacement category.
Embracing versatility, industrial compressors come in various sizes, ranging from compact glove box units ideal for tire inflation to colossal turbo compressors vital in facilitating streamlined pipeline operations.
Power Generation through Air Compression
Air compression elevates pressure beyond atmospheric levels, demanding energy input. Subsequently, as compressed air strives to return to equilibrium, it releases energy while expanding back to atmospheric pressure. This unique process enables air compressors to achieve remarkably high pressures, effectively harnessing potential energy. Notably, compressed air stands out by bypassing the need for energy conversion at the application point. Its hallmark lies in the exceptional power-to-volume or power-to-weight ratio exhibited by pneumatic or compressed air devices.
Despite its inability to match the speed of electricity or the deliberateness of hydraulics, compressed air enjoys broad applications. It often emerges as the preferred choice, especially in scenarios prioritizing cost-effectiveness and efficiency.
The primary advantage of compressed air revolves around the enhanced control it offers, free from the hazards associated with electrical shock or the fire risks linked to oils. Nonetheless, strict adherence to safety codes and regulations governing compressed air handling remains imperative.

Active Air and Energy Air Integration with Geogrid Types
Active air signifies compressed air directly interacting with products, proving invaluable in preserving food, beverages, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries. Conversely, energy air characterizes compressed air utilized for transmitting and storing energy, predominantly powering pneumatic tools and driving mechanical work.
Given the divergence in applications, ensuring superior active air quality becomes paramount, particularly when compared to energy air. Hence, effective filtration plays a pivotal role in eliminating contaminants such as dust, water, or oil. Notably, the integration of diverse geogrid types into compressor structures enhances stability and structural integrity, ensuring robustness in various industrial settings.
Understanding the intricate interplay between industrial air compressors and an array of geogrid materials amplifies their crucial role in ensuring structural reliability and efficiency across diverse industrial applications.